November 9, 2015
BURLINGTON, ON
Alien invaders surround us. They can be found along roadsides. They are common in lakes and rivers. Eventually they will completely over run all natural areas and green spaces.
The alien invaders aren’t people. They are plants, insects, fish, birds, animals and all the non-native species which never existed in a place until they were deliberately or accidentally introduced by people. While some of these alien species are benign, far too many have become invasive and destructive.
Invasive species are a global menace with significant, far-reaching environmental and socio-economic consequences including loss of agricultural productivity and damage to renewable natural resource industries (forestry). Invasive species have caused entire ecosystems to become dysfunctional.

Emerald Ash Bore – This little creature is costing us a fortune – and we are not at all certain we are going to win the battle to stop the infestation.
Hundreds of alien species are currently present in Ontario. Some of the more well know alien invaders include the Zebra Mussel (completely changes a fresh water ecosystem), Emerald Ash Borer (kills native Ash trees) Dutch Elm Disease (nearly wiped out the American Elm) Sea Lampreys (decimated the Great Lakes Trout fishery) and Starlings (crowd out native bird species and cause millions of dollars in agriculture losses each year).
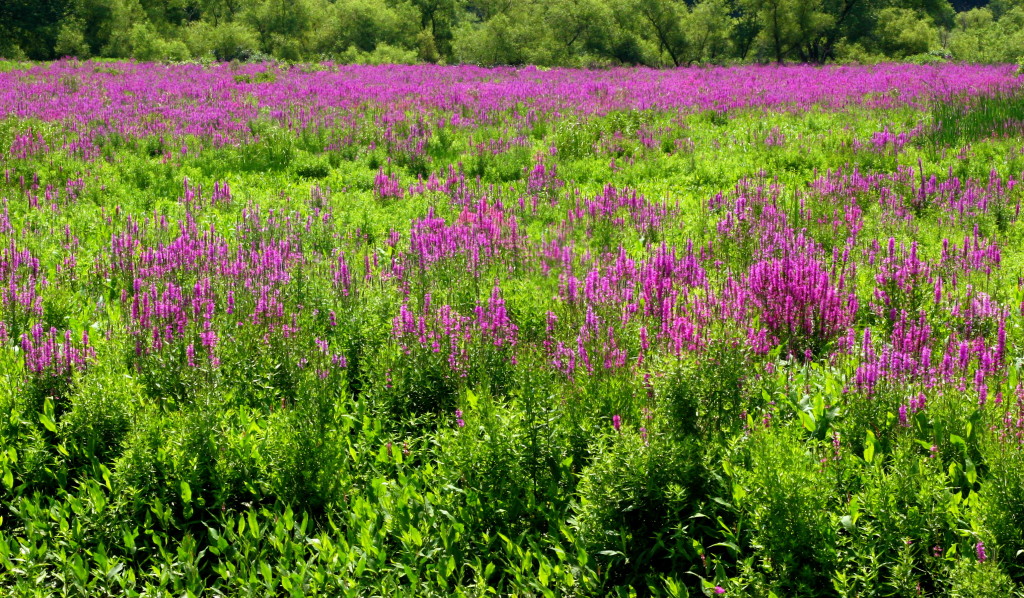
Scientists are fighting back against invasive species, with some successes. Purple Loosestrife (destroyed wetlands) is now controlled by an introduced beetle at the cost of millions of dollars in research. Their decision to release the loosestrife eating beetle was gutsy, considering that a similar effort in Australia to eradicate the invasive Cane Beetle by introducing the Cane Toad was an ecological disaster. While the Cane Toad did eat the Cane beetle, it also ate everything else it could swallow.
Since the Cane Toad had no natural predators in Australia it soon became one of Australia’s most dominant species. The Cane Toad has caused many of Australia’s native insects to become so rare, they no longer contribute in a significant way to the local ecology, with ripple effects on many of Australia’s native plants and animals which have since become rare and threatened with extinction.
The least expensive solutions to the invasive species problems are to prevent problems in the first place and reacting quickly, aggressively and decisively to the first sign of a new invasive species problem.
On November 3rd, 2015, Ontario became the first jurisdiction in Canada to enact a tough law which will reduce the invasive species threat. As per the new Ontario Invasive Species Act, no person shall,
bring a member of a prohibited invasive species into Ontario or cause it to be brought into Ontario;
deposit or release a member of a prohibited invasive species or cause it to be deposited or released;
possess or transport a member of a prohibited invasive species;
propagate a member of a prohibited invasive species;
buy, sell, lease or trade or offer to buy, sell, lease or trade a member of a prohibited invasive species.
bring a member of a restricted invasive species into a provincial park or conservation reserve or cause it to be brought into a provincial park or conservationreserve;
or
deposit or release a member of a restricted invasive species in Ontario or cause it to be deposited or released in Ontario.
First time offenses can result in a $250,000 fine and/or a year of imprisonment. A second offense could cost $500,000. If that sounds excessive, consider that first time corporate offenders could face a $1,000,000 fine with subsequent offenses resulting in fines as great as $2,000,000.
Even though this law’s punitive sanctions don’t fully offset the damages which can result from invasions species, they should sufficient to deter deliberately destructive behavior.

Snow-On-The-Mountain (aka Goutweed) is a robust ground cover that will eventually become Ontario’s most dominant forest plant.
Ontario’s new Invasive Species law will affect many local nurseries and gardeners. Several common ornamental plants which have been sold in local nurseries for decades are known invasive species problems. Snow-On-The-Mountain (aka Goutweed) is a robust ground cover that will eventually become Ontario’s most dominant forest plant. Goutweed will displace most of Ontario’s native forest species, including Trilliums which are our provincial flower. Goutweed is a likely early candidate for the invasive species list.
Another problematic invasive ornamental plant is Mountain Fleece (aka Japanese Knotweed). The roots of this tenacious alien species can destroy driveways and cause structural to buidings. Once established, Japanese Knotweed is nearly impossible to permanently eradicate. Eventually this plant will replace most native plant species growing along Ontario’s shorelines.
Both Goutweed and Japanese Knotweed have escaped cultivation locally. They are commonly found throughout Burlington’s green spaces along with invasive Himalayan Balsam, Garlic Mustard, Phragmites and Buckthorn.
These invasive species are not just serious ecological problems here in Ontario; they are also serious global ecological problems which affect natural areas near London England, Sapporo Japan, Christchurch New Zealand, Pretoria South Africa and every other ecosystem on the earth which shares similar climate and conditions as Burlington. Deliberately cultivating this species in the UK is illegal and can result in substantial fines.

Japanese knotweed – seen all over the place in Burlington. Fiorito believes that once established, Japanese Knotweed is nearly impossible to permanently eradicate.
The mere presence of Japanese Knotweed in a neighborhood lowers everyone’s property values. British Real Estate law now requires home sellers declare the presence of Japanese Knotweed on their property. If this plant is subsequently discovered on that property, then the buyer can sue the seller for eradication costs.
In Burlington, Japanese Knotweed is available at many local nurseries. Many local gardeners have unwittingly created problems that will be expensive to fix, when Japanese Knotweed is inevitably put on the invasive species list.
The easiest way that gardeners can avoid creating invasive species problem around their homes is to choose plant species which are native to the local ecosystem. Each spring the Royal Botanical Gardens holds an annual native plant sale. Most nurseries now have a native plant section. Several local nurseries and landscape designers have become native plant specialists. This new invasive species law will help forward looking local businesses grow and prosper.
We can no longer ignore the destructive consequences of invasive alien species anymore. Failure to consider the ecological consequences of introducing an invasive alien species will become expensive in the not so distant future. This new law will help change attitudes leading Ontarians to becoming better stewards of the natural systems which rejuvenate our soils and clean our air and water. Ontario’s new invasive species law represents real change and will help protect Ontario from the growing international invasive species threat.
 Vince Fiorito is the steward of Sheldon Creek; a designation given him by Conservation Halton. He was recently a candidate for the Green Party and is an extremely knowledgeable person when it comes to what we are doing to our environment. Don’t get him going.
Vince Fiorito is the steward of Sheldon Creek; a designation given him by Conservation Halton. He was recently a candidate for the Green Party and is an extremely knowledgeable person when it comes to what we are doing to our environment. Don’t get him going.