By James Smith
By James Smith
March 7, 2015
BURLINGTON, ON
Sometimes, little noticed somewhat boring announcements by government are the ones that pack the biggest punch. Yesterday’s announcement by Minister Ted McMeekin that Ontario intends change to how we’ll plan, build, and pay for developing cities in Ontario is one such announcement.
The way Ontario is built and developed is about to change; I think this will be a very welcome. First let me declare my bias, I’m a Founding Member of BFast (Burlington for Accessible Sustainable Transit), and as a design consultant I often work on projects for both public and private developers. I feel the changes announced by Minister McMeekin yesterday may mean modestly more work for me and my clients.
If these changes live up to the billing, changes to Smart Growth, land use planning and development charges have the potential to be a seismic shift on how cities are built for years to come and this affects us all. The coming changes will radically impact how we go about urban growth in Ontario on a scale as large as the introduction, ten years ago, of The Green Belt. If the legislation lives up to the press release, the Province will put teeth into its Smart Growth policy and Municipalities will need to pull their weight.
So far Smart Growth is a policy many municipalities, including Burlington, give just lip service. Professional planners and drafters of Official Plans write elegant documents, but City and Town Councils frequently ignore their more lofty goals. With this legislation Minister McMeekin is saying Municipalities will be held to account, and will need to live up to the Goals of Smart Growth. Long overdue.
 This change is about the kind of building projects we’ll see built in Ontario and how we will pay for the stuff we build. I suspect that members of Burlington and other City councils who subscribe to the failed dogma of Libertarianism won’t like this legislation one bit. To them I say: “suck it up princess, the free ride is over”. Specifically these Planning Act Changes propose to:
This change is about the kind of building projects we’ll see built in Ontario and how we will pay for the stuff we build. I suspect that members of Burlington and other City councils who subscribe to the failed dogma of Libertarianism won’t like this legislation one bit. To them I say: “suck it up princess, the free ride is over”. Specifically these Planning Act Changes propose to:
• Ensure residents are better consulted at the beginning of the planning process for new developments.
• Encourage residents to provide feedback on the future of their communities.
• Help municipalities resolve potential planning disputes earlier, reducing involvement of the Ontario Municipal Board in local disputes.
• Extend the review of new municipal official plans to 10 years, instead of the current five-year cycle
• Providing municipalities with more control and stability over their planning documents. Once a municipality establishes a new official plan, it would be frozen and therefore not subject to new appeals for two years unless changes are initiated by the municipality. A community planning permit system once established by a municipality would not be subject to any appeals of private applications for five years.
• Clearly defining what constitutes a minor variance (a small change from a zoning bylaw).
Better consultation with residents early in the development process and getting their feedback are welcome, long overdue changes. The challenge will be to break down the walls of NIBYism; no small task. For at least seventy years North America has embraced suburban sprawl funded by, more sprawl.
Leigh Gallagher, in her book The End Of The Suburbs outlines how North Americans have the car-centric suburban landscape in their DNA and is our expectation of where we live. Both Gallagher and Smart Growth talk about breaking this unsustainable cycle. The proposed changes to the Act will have to help with this understanding of what Smart Growth means, so residents will need to understand this shift when proposals are brought forward. As, or more importantly, the development industry will have to change their business model too.

Six houses identical to this one were torn down on land that was part of the Veterans Land program – the lots were assembled and the infill shown below built.
Boilerplate infill projects will no longer be acceptable. Projects will more and more have to reflect an individual neighbourhood’s character and residents taste and long-term expectations for their community. Budgets for new projects will therefor need to change as removing the hated OMB from most planning disputes will mean more money being spent on public meetings and Architects’ fees and less time on Lawyers’ fees. In my experience, anytime more thought goes into a design and less time is spent on legal wrangling makes for a better project.
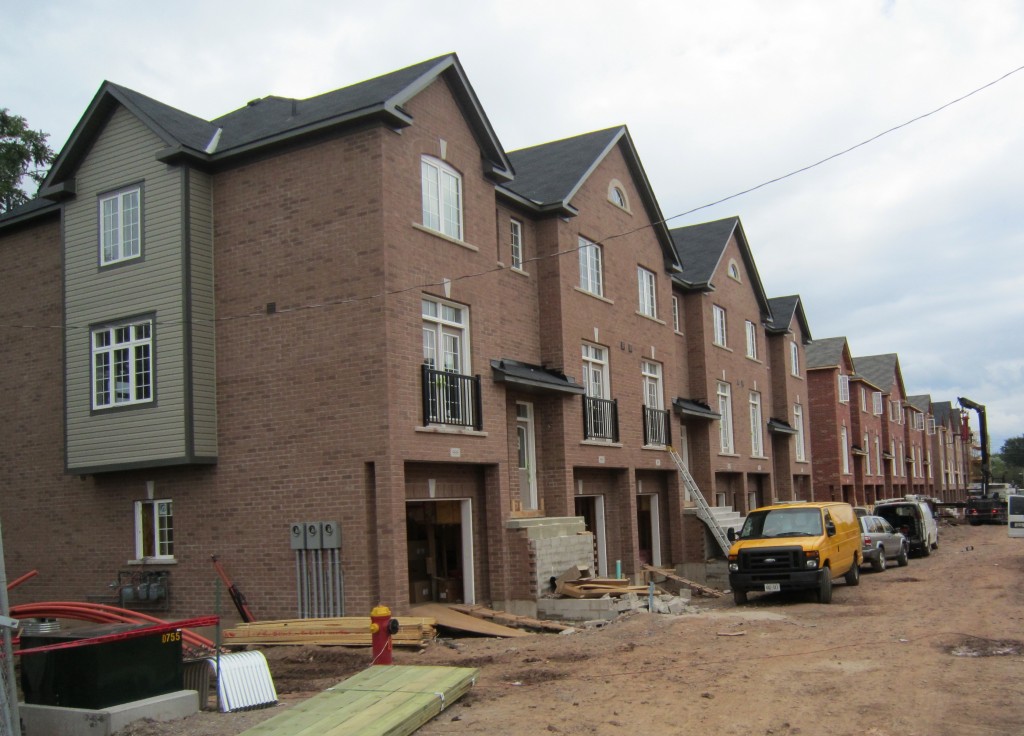

Fifty eight units were built on land that previously had six homes on it. Tough to find a back yard in this infill project.
The ten year cycle for Official Plans has potential positive benefits as it will reduce the time Cities and Towns spend on Official Plans and free up those staff resources. No only is limiting the involvement of the OMB of great news, these changes will mean fewer Municipalities, will do their city planning by Official Plan Amendments. Burlington specifically has for at least 25 years engaged in planning by Official Plan Amendments rather than relying on either the Regional or City’s Official Plan. Councils often are blinded by developments that have actually cost the Municipality money in the long run as the Official Plan Amendments often is at odds with the official plan, these changes will force the Development industry to do better planning, spend more on Designers and less on Lawyers.
Development Charges are set to be changed in the following fashion:
• Help municipalities recover costs for transit services and waste diversion.
• Create clear reporting requirements for capital projects municipalities financed though development charges, as well as section 37 of the Planning Act related to density bonusing and parkland dedication.
• Municipalities would be required to follow reporting requirements that reflect best practices and detail to the community how money from development charges is spent.
• The government would create better reporting requirements for municipalities collecting money under section 37 of the Planning Act related to density bonusing, and related to parkland dedications, which details how the funds are spent.
• Development charges would be payable at the time the first building permit was issued for a building so that developers could be certain of the cost.
• Municipalities would be required to better integrate how development charges fit with long-term planning, including local asset management plans.
• The government will help municipalities identify and share their best practices on using development charges to address local planning and financial objectives.
• There would be more stringent reporting and greater oversight of any funds or municipal charges on new developments that fall outside what is allowed in current legislation
Development Charges can be a useful tool to reflect the real capital costs of any building project on a municipality. Planner Pamela Blais in Perverse Cities clearly outlines that the real cost to the municipal taxpayer of urban sprawl is not presently accounted for in many North American jurisdictions. Development Charges attempt to make a project pay for the real cost of the capital costs a new project represents.
While Transit and Waste diversion were not specifically accounted for in the previous Act they can be funded under more general categories. Specifically calling these items out is a good step. The challenge will be to use Development Charges to limit Greenfield, or make it pay for the burden it puts on a Municipality while simultaneously not acting as a brake on positive and creative infill development.
So there needs to be the ability for Municipalities to bracket Development Charges accordingly.